Student Finance Guide UK 2024

Student finance is often a huge part of higher education for the majority of students in the UK. On average, graduates leave university with a debt of £45,600 as of 2022/23. Despite this, recent studies have shown that there's a significant gap between the impact of the debt and the actual understanding among affected individuals. Our guide provides an in-depth overview of student loans in the UK, covering topics such as loan types, application procedures, repayment methods, recent changes, trends, and the broader landscape of student finance. You'll also find practical resources and some top tips for managing loans effectively.
The Governing Bodies
Depending on where you went to university, your loan will be managed by a governing body. The exception being pre 1998 loans which are managed by private loan companies.
Student Finance England (SFE): If you're in England or sometimes Wales, and have taken out a student loan through the government, you typically make repayments through Student Finance England. You can manage your account and make payments online through their website.
Student Finance Wales (SFW): For most students in Wales, Student Finance Wales handles the repayment process for student loans. Similar to SFE, this is an alternative where you can manage your account and make payments through their online portal.
Student Awards Agency Scotland (SAAS): In Scotland, the Student Awards Agency Scotland manages student loans. Borrowers can make payments and manage their accounts through the SAAS website.
Student Finance Northern Ireland (SFNI): For students in Northern Ireland, student loans are managed by Student Finance Northern Ireland. Borrowers can access their accounts and make repayments through the SFNI portal.
Student Finance Repayments: Key takeaways
Here is a quick list of the main factors that impact student loan repayment:
Repayment threshold: You start repaying your Student Loan once you have finished your degree, and are earning the set threshold and above - these vary from country to country so check your plan below.
9% rule: You only pay 9% of earnings over the threshold, not the full amount.
Continuous interest: Interest accrues daily, from the day you take out your first payment, even if you're not making repayments yet.
How it is paid? Repayments are deducted from your wages automatically once you earn over the threshold. Self-employed individuals will need to repay directly and this is observed in your self assessment.
Loan write-off: Monthly repayments continue for 25, 30, or 40 years until the loan is fully repaid or canceled.
Changeable terms: Loan terms, including interest rates and thresholds, can be altered even after signing the contract.
The 5 Repayment Plans
In the United Kingdom, there are five types of student loan plans: Plan 1, Plan 2, Plan 4, Plan 5 and Postgraduate loans. You can be on more than one plan at a time i.e. Plan 2 and Postgraduate, in which case there can be slight overlaps in how you repay your loan. Read more on overlapping plans.
Plan 1 Loans: Plan 1 loans are designed for students who started their undergraduate courses between 1998 - and September 2012. Under Plan 1, repayments begin once the borrower's annual income exceeds £22,015. They will be expected to repay 9% of any income over this threshold. The interest rate is determined by either the Bank of England base rate plus 1% or the rate of inflation, whichever is lower. Plan 1 loans are automatically written off after 25 years if the first loan was taken on or after September 1, 2006; otherwise, the loan is written off when the borrower turns 65.
Plan 2 Loans: Plan 2 loans apply to students who started their undergraduate studies after
September 1, 2012. Repayments begin when the borrower's income surpasses £27,295 per year, with repayments
amounting to 9% of income above the threshold. The interest rate typically follows the Retail Prices Index
(RPI) plus a percentage. The percentage is worked out depending on your earnings (example below) however
it's currently capped at 7.8%. Plan 2 loans are automatically written off after 30 years starting the April
after you graduate.
Practical example:
- If you earn less than or equal to £27,295/year. Interest rate = RPI
- If you earn over £49,130/year. Interest rate = RPI + 3%
- If you earn between £27,296 to £49,130. The extra on top of the RPI moves from 0% to 3%. For example, earn
£38,213 which is halfway and your rate will be RPI + 1.5%.
Plan 4 Loans: Plan 4 loans are for students applying to the Student Awards Agency Scotland. The repayment threshold for Plan 4 loans is £27,660 per year, with borrowers repaying 9% of income over this threshold. The interest rate on Plan 4 loans is 6.25%. Plan 4 loans are automatically written off 30 years after April the borrower was first due to repay if the first loan was taken on or after August 1, 2007; otherwise, the loan is written off when the borrower turns 65 or after 30 years from the April they were first due to repay, whichever comes first.
Plan 5 Loans: Introduced for students beginning courses on or after August 1, 2023, Plan 5 loans offer repayment terms tailored to the needs of eligible students. The repayment threshold for Plan 5 loans is £25,000 per year, with borrowers repaying 9% of income over this threshold. The interest rate on Plan 5 loans is 7.8%. The biggest difference with Plan 5 loans is they are automatically written off 40 years after the April the borrower was first due to repay as opposed to 30 years for most other plans.
Postgraduate Loans: Postgraduate loan plans are aimed at students pursuing Master's or Doctoral courses. The repayment threshold for Postgraduate Loan Plans is £21,000 per year, with borrowers repaying 6% of income over this threshold. The interest rate on Postgraduate Loan Plans is 7.8%. Postgraduate loan plans are automatically written off 30 years after the April the borrower was first due to repay.
| Plan type | Yearly threshold | Monthly threshold | Weekly threshold | Interest rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plan 1 | £22,015 | £1,834 | £423 | 6.25% |
| Plan 2 | £27,295 | £2,274 | £524 | 7.8% |
| Plan 4 | £27,660 | £2,305 | £532 | 6.25% |
| Plan 5 | £25,000 | £2,083 | £480 | 7.8% |
| Postgraduate Loan | £21,000 | £1,750 | £403 | 7.8% |
Overlapping Plans
Maybe you did a Master's, or you revisited a degree some years later, no matter, it's pretty straightforward.
Without Postgraduate Loan: If you have more than one loan plan but no Postgraduate Loan, you repay 9% of your income over the lowest threshold among your plan types. This results in a single repayment per pay period.
Suppose you're on Plan 1 and Plan 2, earning £25,200 annually. With a monthly income of £2,100, you'll repay 9% of your earnings over the lowest threshold, which is £1,834 for Plan 1. The calculation yields a monthly repayment of £24.
With Postgraduate Loan: If you have a Postgraduate Loan along with other plan types, you'll repay 6% of your income over the Postgraduate Loan threshold and 9% over the lowest threshold for other plans.
Consider having a Postgraduate Loan and a Plan 2 loan with an income of £28,800 annually. With a monthly income of £2,400, you'll repay 6% of your earnings over the Postgraduate Loan threshold (£1,750) and 9% over the Plan 2 threshold (£2,274). The calculations result in a total monthly repayment of £50.
How much does university cost in the UK?

9000 x 4 = ?
For tuition, it costs £9,250 in England, £9,000 in Wales and varying amounts in Scotland and Northern Ireland depending on which university you went to. Therefore, in its simplest form, you can multiply the length of your course by the fee and hey presto! you have a cost for the university. However, if like most people, you borrow the tuition and/or maintenance loans you will be enrolled to pay back these loans plus interest using one of the 5 plans we mentioned before.
Debt, Income and Thresholds
On average, graduates leave university with £45,600 in debt, as uncovered in this report from the UK government published late 2023 - UK Student loan statistics. This is most commonly repaid in monthly chunks which are based on your income. This is to ensure that you only pay back what you can afford. Two factors determine your monthly payments, the plan's threshold and your income. You pay back on anything you earn over the threshold and of that, you pay back 9% of this. This is paid through the Pay As You Earn (PAYE) scheme if you work in the UK, else you will need to make payments directly to Student Finance England.
For example, you earn £30,000 and you are on Plan 5. You would do £30,000 - £25,000 (Plan 5's yearly threshold) which equals £5,000 and then multiply this by 0.09 to get 9%, which is £450. In this example, you will pay back £450 over the year which is £37.5 a month (450/12).
In the unlikely event, that your salary and the plan threshold stay the same, you can extrapolate by the number of payback years. Returning to the example, plan 5 has a 40-year payback period by which you will have paid £18,000 towards your loan (450 x 40). Any remaining balance, including interest, will be wiped. Sounds good right? After all, this is considerably lower than the average total debt and the observant of you may have already worked out that, in this scenario, a university degree will have only cost you £4,500 per year all in, based on a 4-year course. What a bargain.
However, before you raise a toast to your victory it's important to consider several factors that will impact the true final cost. Most important is your income and the idea that it will go up, ideally by a significant amount. Other factors include interest rate changes, inflation changes, threshold changes, employment changes and government policy changes. With this in mind, it becomes apparent that accurately assessing the true cost of university is far from straightforward. To demonstrate this we used the The Student Finance Calculator and plugged in the same numbers.
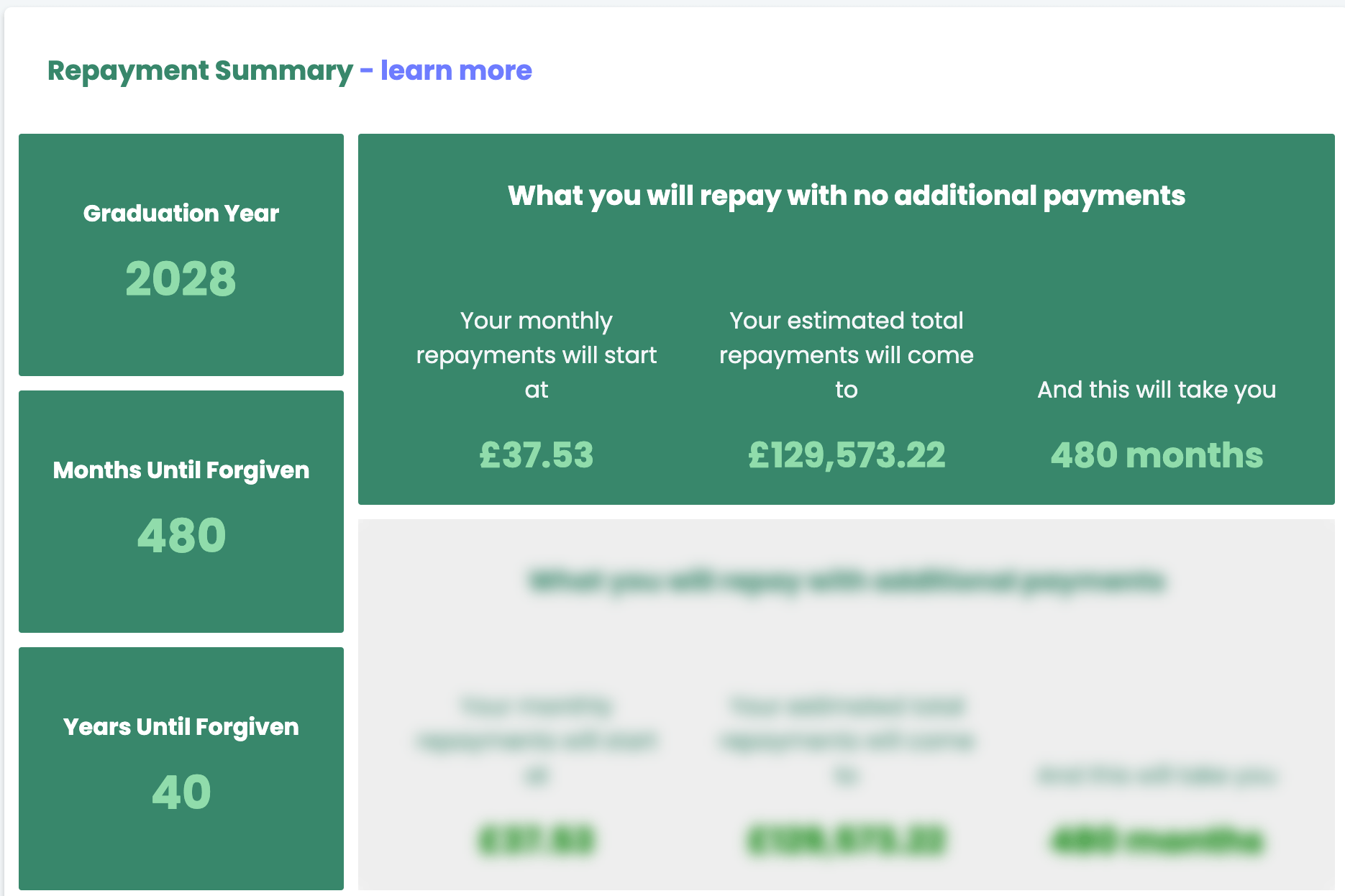
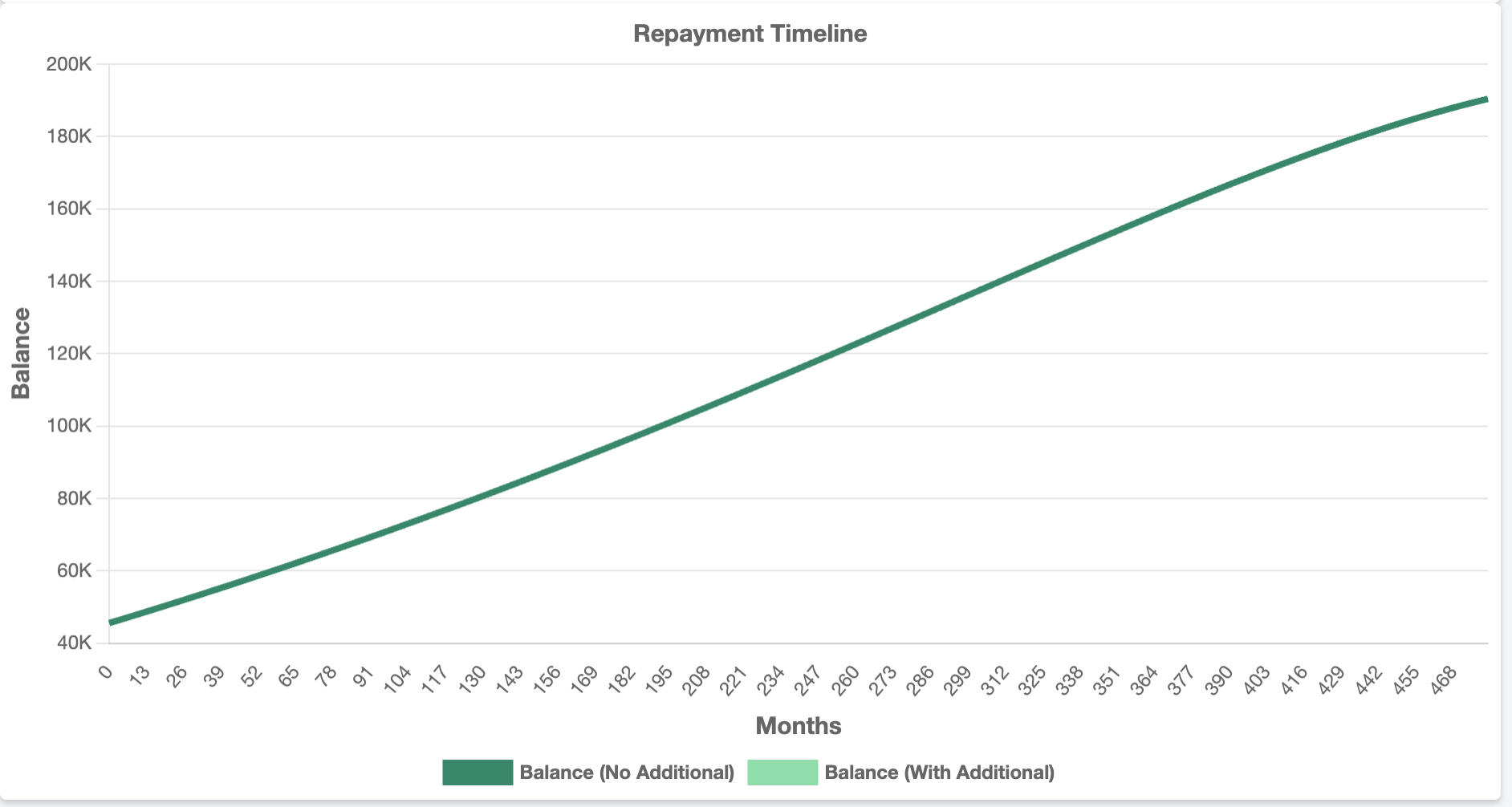
As you can see the calculator has got the monthly repayments the same as our previous calculations but the total repayments are above and beyond £18,000, coming in at a staggering £130,000. Why you ask?
Wage Growth
Just a 4% increase in your wages each year compounds to reach an almost questionable £150,000 salary in 40 years. This may seem unattainable but factoring in inflation this is akin to earning £50,000 in today's money. Bigger salary = bigger monthly payments = bigger total repayment.
Inflation and thresholds
Another important influencer of this total repayment amount is the repayment thresholds that each plan has. The government increases the thresholds according to inflation and since a higher threshold means a smaller amount of your salary is considered for monthly repayments you effectively pay less each month. The Bank of England aims for 2% inflation and often can achieve this, so we have set this to 2% in our calculations.
One straightforward approach to understanding the influence of thresholds on your monthly repayments is to envision the threshold set at zero. In this scenario, your monthly repayments would represent 9% of any amount exceeding zero, essentially your entire salary. Consequently, 9% of your total salary is naturally greater than 9% of a fraction of your salary. Thus, if your salary remains constant and the threshold rises, your monthly payments will decrease.
Conclusion
In conclusion, if you borrow to pay your tuition fees, university costs what you can afford and it is different for everyone. Practically speaking the interest accrued and the total debt is irrelevant unless you expect you will pay back your loan in full. Some say, that instead of looking at it as a fixed cost, it should be considered an education tax that students have to pay in return for higher education. If you get a high-paying job you pay more for the education than lower earners, most of the time.
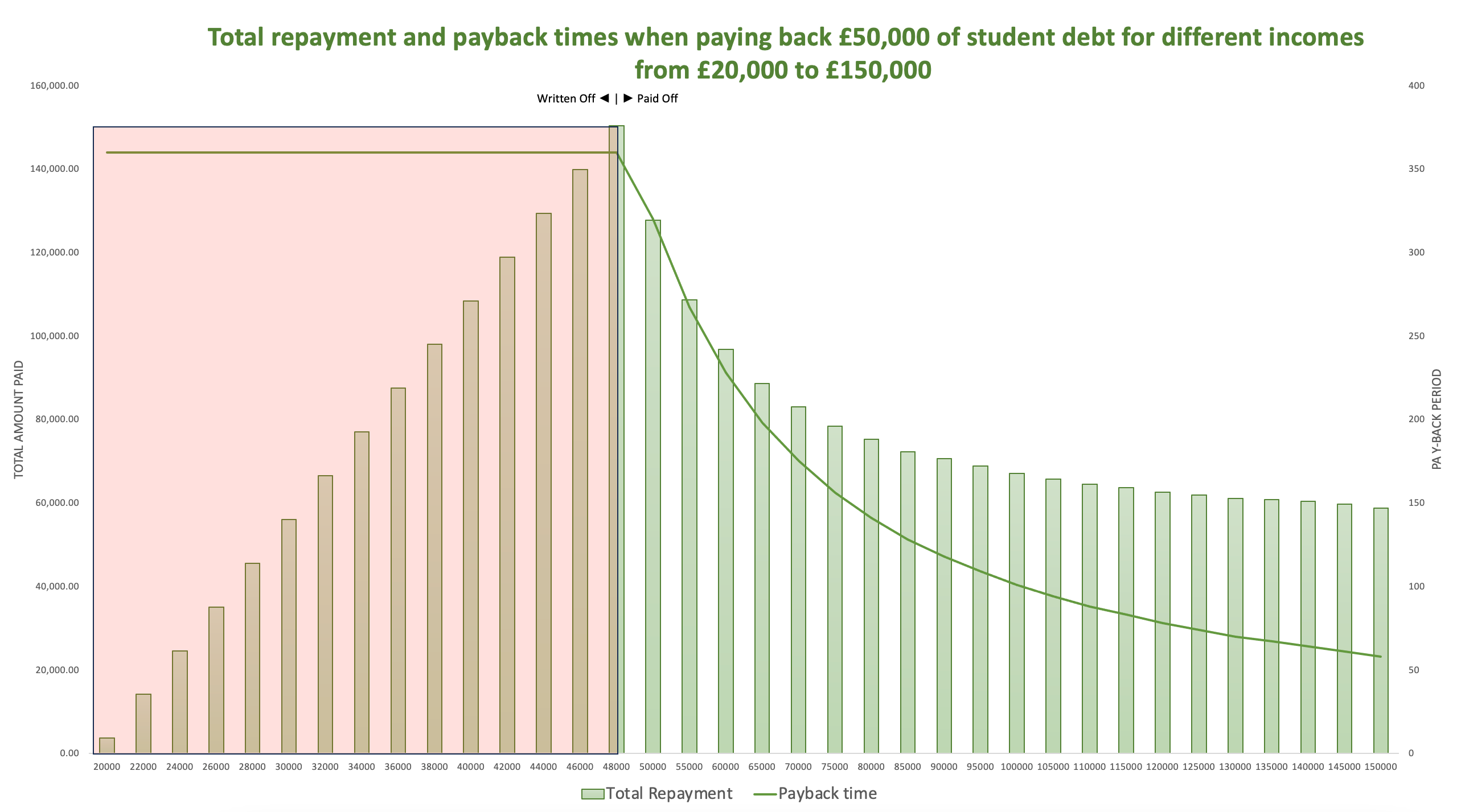
The caveat
It is true that the more you earn the more you pay for university, however, there is a tipping point where this trend reverses. Student Finance Loans like any other loan can be paid off. If you are a high earner, or you borrowed less money, or both, you may be predicted to pay off your loan before your termination date. In these scenarios, it starts to favor larger monthly payments over smaller ones. This is simply because larger monthly payments will get your loan to 0 faster and thus save you on interest accruals. With this logic, it can be seen that higher and higher earners start to pay less and less for their student loans past a certain point. It is important to remember that in these scenarios they are paying less relative to what they are obligated to pay. This does not mean that it is less than what you are obligated to pay. Not everyone should try and 0 their loans as for most this will only end up costing you more. Moreover, high earners can afford these higher payments whereas, for middle to low earners, this capital could be better used elsewhere.
Low, middle, and high earners is a relative term and is not related to any number. There are many factors that go into making decisions on overpaying on your loan. We have an article on what to consider when Paying Student Finance Back Early
What if you have more than one job?
Having Multiple Jobs: If you hold more than one job, repayments are based on individual job incomes surpassing the threshold for your specific loan plan, not the combined income across all jobs
Example 1 (Plan 1 Loan): Let's say you have two jobs and a Plan 1 loan. One job pays £1,000 per month, and the other pays £800. Since neither income exceeds the £1,834 monthly threshold, no repayments are required
Example 2 (Plan 2 Loan): Suppose you have a Plan 2 loan and two jobs. Job A pays £2,300 monthly, while Job B pays £500. Repayments are made only on the income from Job A, which exceeds the £2,274 threshold
What if you're self employed?
Self-Employment: For self-employed individuals, HM Revenue and Customs (HMRC) calculate annual repayments based on tax returns and total yearly income. If repayments have already been made from salary, HMRC deducts them from the total repayment amount.
What if you're overseas?
If you're considering an extended period of work or travel abroad, there are important factors to consider
regarding your student loan repayments. Depending on your repayment plan and your location abroad, you may
still be required to make repayments above certain income thresholds. You'll need to determine your specific
threshold and arrange manual payments accordingly. For stays abroad exceeding three months, repayments must
be made directly to the Student Loans Company (SLC). Notify SLC before departing the UK to avoid potential
issues later. SLC will request income details to calculate monthly repayments, converting your income into
pounds sterling. You'll be responsible for any currency conversion fees and bank charges associated with
transferring funds to SLC. While repayment rates mirror those in the UK, living costs abroad may lead to
different repayment thresholds.
Overseas
Thresholds Plan 1
Overseas Thresholds Plan 2
Overseas Thresholds Plan 4
Overseas Thresholds Postgraduate
What happens if you miss any repayments?
It's important to meet your loan repayment obligations as outlined in the loan agreement and regulations. If you miss payments, the Student Loans Company (SLC) has the authority to take legal action to reclaim the debt. This could involve obtaining a court order for you to repay the total amount owed, including interest and penalties, in one payment. This legal process applies whether you're in the UK or residing abroad, and you'll be responsible for covering all associated costs, including legal fees. If you do or already have missed payments the best thing to do is to just pay back what you have missed and get your account out of a delinquency
How to contact Student Finance
To get information that is specific to your situation you will need to get in contact with the governing body you live in (or where the uni resides if you don't live in the UK)
England
Phone: 0300 100 0607
Twitter: @SF_England
Website: Student
Finance England
Northern Ireland
Phone: 0300 100 0077
Website: Student
Finance Northern Ireland
Scotland
Phone: 0300 555 0505
Twitter: @saastweet
Website: Student Awards Agency
Scotland
Wales
Phone: 0300 200 4050
Twitter: @SF_Wales
Website: Student
Finance Wales
Student Finance Company
Student Finance Company
Student Finance Trends in the UK
Recent reports indicate a significant escalation in average student loan debt. Questions about interest rates, affordability, students' long-term financial well-being, and repayment are top of mind. We explore key trends, interest rate dynamics, comparative analysis with international standards, and potential implications for policymakers and students.
Trends in Loan Debt: The scale of student loan debt in the UK is staggering, with approximately £20 billion loaned annually to around 1.5 million students in England alone. By March 2023, the value of outstanding loans had surpassed £206 billion, with forecasts projecting a rise to £460 billion by the mid-2040s. This escalation is attributed to a shift in government funding policies, increasingly relying on loans to finance maintenance and teaching expenses.
Interest Rates: Interest rates play a pivotal role in determining the affordability of student loans. For post-2012 loans, including Plans 2, 3, and 5, interest rates peaked at 7.5% by the end of 2023, significantly impacting the long-term cost of borrowing. In contrast, Plan 1 loans, applicable to students enrolled before 2012, are linked to the Bank of England base rates, with an interest rate of 6.25% for the 2023/24 academic year.
Average Debt: Forecasts indicate that students embarking on their courses in 2022/23 will face an average debt of £45,600 upon completion. However, reforms implemented in 2022 expect to reduce this figure to £42,900 for students entering the reformed system from 2023/24 onwards. Despite these projections, government estimates suggest that only 27% of full-time undergraduates starting in 2022/23 will repay their loans, a figure expected to rise to 61% following the extension of the payback period to 40 years.
Rates and Trends: Interest rates for student loans have experienced significant fluctuations in recent years, with Plan 1 and Plan 2 loans reaching levels of 6.25% and 7.5%, respectively, in 2022/23. Furthermore, the growth in maintenance loans for full-time students in England alone reached £8.3 billion in 2021/22. These factors have significantly added to the overall outstanding student loan debt, and thanks to steady interest rates and increasing living expenses, this debt will likely continue to rise.
Comparative Analysis: Comparative analysis with international standards reveals that student loans in England are substantially higher in magnitude compared to other countries analyzed by the OECD. This disparity underscores the unique challenges and complexities inherent in the UK's student finance system, necessitating careful consideration and evaluation of policy interventions and reforms.